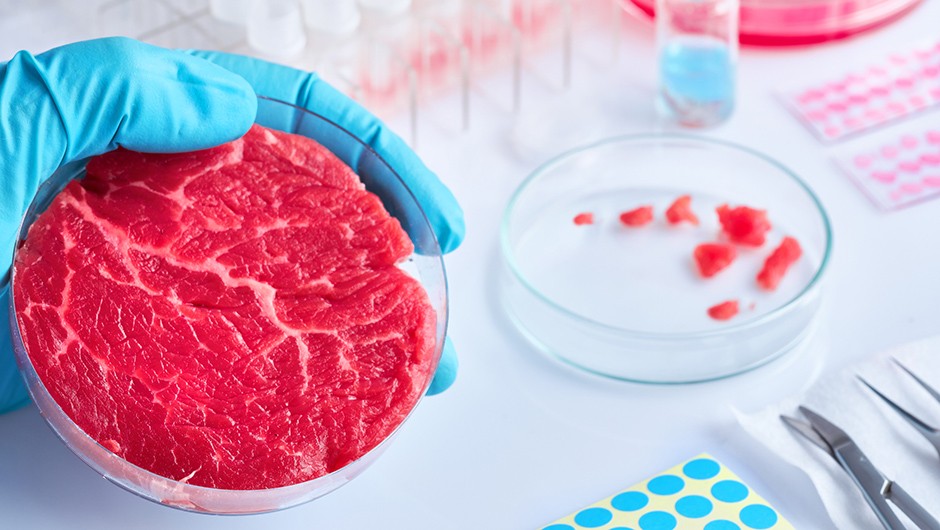
Cultured meat can also be referred to as in-vitro meat, clean meat, lab-grown meat, manufactured, or synthetic meat.
How is lab-grown meat made?
It is produced from extracted animal cells which are cultured in a container and grown into thousands of muscle fibers that form a piece of meat.
Lab-grown meat has been forecasted in the time past and with the move to conserve animals, which has birthed the idea of veganism, cultured meat seems to have come to stay in 2020 and beyond.
There is now strong anticipation in the commercial food industry that manufactured meat will be available in food stores soon.
While some stakeholders in the food industry believe lab-grown meat will be safe and possibly better for human consumption than slaughtered meats, this assertion can not be justified yet.
While synthetic meat will help in preventing animal extinction, minimize the spread of some animal diseases to humans, nobody knows about the long-term effects of cultured meat.
Lab-grown meat production will have some economic effects, one of which is unemployment.
Due to the production process, it will be expensive and maybe deficient in nutrients when compared to meat from live animals.
These cultured meats are also very similar to genetically modified animals which have gained mixed reactions in terms of safety and health benefits.
Some questions have arisen concerning this industrial meat and its cost.
While vegans may embrace this, the concern is that, would this be available for common men since the cost will be high compared to meat from live animals.
Advantages of Cultured Meats
There are potential benefits clean meat may offer society, let’s look into some of the advantages.
- It will reduce animal suffering
While I strongly believe cultured meat will not replace traditional meat, and it does not end animal cruelty, it will make some differences.
As human populations increase and the need for more protein, the rate of animal slaughtering for food has also increased.
Animals are mostly raised for food consumption and to get industrial materials, and these animals are raised in confined, small spaces, and through completely unnatural feeding methods which make them suffer a lot even before they are killed.
Although cultured meats are produced from stem cells of live animals, and such animals will lose their life in the process, more meats can be produced from fewer animals with cell-cultured meat.
- Transmission of diseases from animal to human can be prevented
Many harmful bacteria and parasites in animals complete their life cycle in humans when they are eaten.
This causes a series of food-borne diseases such as Norovirus, Coccidiomycosis, Clostridium perfringens, Psittacosis, Staphylococcus aureus, Histoplasmosis, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Trichinosis, Blastomycosis, and many others.
These Zoonotic diseases are becoming more popular in the last decade because of how less we’re careful with the breeding of this animal and less effective regulations are in producing meat for human consumption.
Even though the major causes of foodborne diseases are being addressed in the US today, a transition to cultured meat will reduce the rate of foodborne and food contamination diseases significantly.
Weighing the economic and health risk of food-borne diseases and the health risk of cultured meat, the economic effects of a disease outbreak on lives, government intervention on it, and the destruction of these meats will be far more than the yet unverified health risks of clean meat.
- Cultured meat is energy saving
Animals being reared for food occupy space and generate greenhouse gas emissions. Statistics have shown that animals contribute not less than 15% of global gas emissions, and their contribution is more than automobiles.
Livestock, which is the major source of protein produce feces which leave much of methane and nitrous oxide in the ecosystem
Animal use of much of landmass is also a contributing factor to deforestation, water pollution, and others. However, cell-cultured meat will not require much land and water and would require less energy to produce an equivalent amount of traditional meat.
Conclusion
Along with the advantages of adopting lab-grown meat, there is also a possible threat, especially in the long run, and studies and facts about these possible inherent risks are not yet well established.