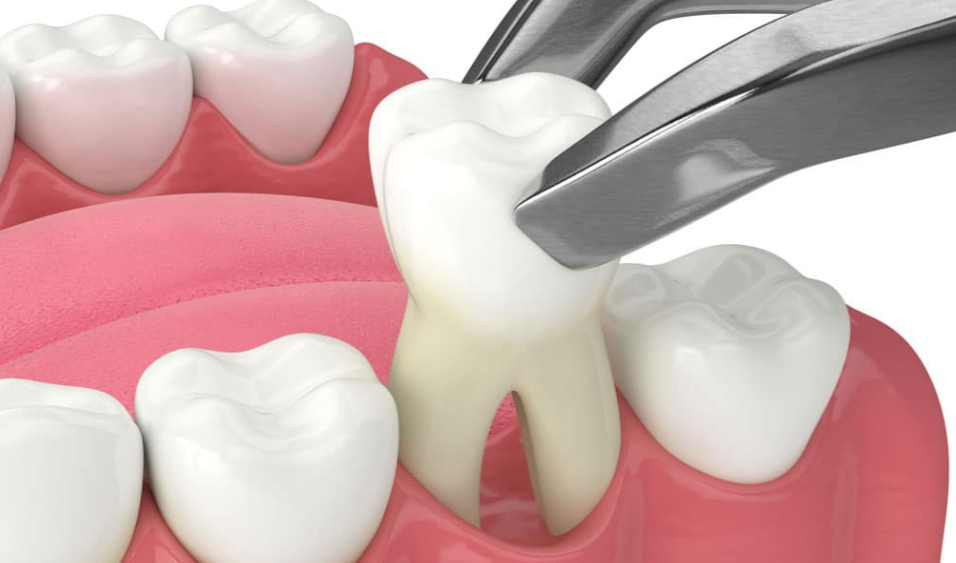
Tooth decay is a common reason for tooth loss and extraction. While the pain can be minimal if you lose any of your teeth naturally, tooth extraction can cause problems.
If you lose your tooth by an accident, there can be damage to your gum and nerves, and the trigeminal nerves can cause a serious tingling sensation in your mouth.
There are dos and don’t after tooth extraction. For example, things you should avoid after tooth extraction are alcohol, spicy foods, hard foods like bread, hot drinks, sucking, sipping, etc so the gum can heal faster.
It takes 3 days to get relief after tooth extraction when the gum closes off the hole, and you can recover fully after 1 month.
Your surgeon would tell you to take rest for a whole day, avoid taking anything, including water, and after 24 hours, you should take a lot of water to keep hydrated and to promote healing.
What are the Side Effects of tooth Extraction?
There are side effects to expect after tooth extraction, but it’s relatively safe if you consult a qualified dental surgeon.
- Tooth extraction can cause pain and headache when the socket is inflamed.
- Dental anesthesia you’re placed during tooth extraction can have side effects on your eyes such as blurred vision, meiosis, diplopia, etc.
- Bleeding at the extraction site can occur within 1 to 2 days.
- Swelling and changes in your facial skin can also occur and fade off after some days
- Infection can also occur when foods get stuck and food debris triggers bacteria growth at the extraction site.
Long-Term Side Effects of Tooth Extraction
Misalignment of Teeth
One of the long-term effects of tooth extraction is that, over time, other teeth near the cavity will be displaced due to grinding and chewing.
Your teeth support one another, and when one is removed without any replacement, others become loosened, and it leads to misalignment of the teeth.
Over time, the misalignment will cause pain, making biting difficult, and can lead to damage to other teeth.
It also makes other healthy teeth around the hollow created by extraction chip, break, or fracture after some time.
Once a tooth is removed, the other teeth should be adjusted, or the hole should be filled with a bridge or artificial tooth to minimize the level of misplacement.
Pain and Migraine
The teeth below and above the dental extraction spot can be loosened after some years, and it can cause serious pain again.
The movement of the teeth from their positions can also cause changes to the structure of jaw bone and functions and cause migraine.
You can also feel pain in your head and face, from the jaw, nose cavity, eye socket, and neck, and have more health challenges, including temporomandibular disorders.
Reduced Functions of the Teeth
Teeth perform well while in a set, but when one tooth is removed, other teeth near the socket function less since you’re avoiding the area while eating.
Also, it reduces the biting and grinding functionalities of the teeth near the extraction spot, and increases the chewing load on another side where there’s no tooth extraction.
This can trigger teeth decay and more dental extraction in the future if care is not taken.
Problem with Chewing food
If you’re not able to chew foods properly, then it can have a serious impact on your diet, nutrition and healthy living.
Dental extraction and loss can make you feel reluctant to eat since you’re using more side of the teeth, and it can cause strain to your face.
Foods that are stuck in the tooth socket can also increase food debris, cleaning, or infections.
Your inability to chew as much as you’d like to means you can be avoiding healthy foods, which can trigger nutrient deficiency and illnesses.
Loss of vertical dimension of occlusion
One of the premolar extraction side effects is bite collapse. This occurs when 2 or more of the molars have been extracted in the past, and you’ve lost the vertical height between your upper jaw and lower jaw.
This simply means the cusps of your teeth will be resting on each other.
Also, the jaw bones and muscles around extraction will be weakened and will not be able to withstand regular chewing, and teeth begin to tip sideways, causing crapped and chapped lips due to the bite collapse.
Low self-esteem and Confidence
Another long-term side effect of exodontics is the changes it brings to your appearance and beauty, and the negative effects on your emotional health.
You may feel you’ve lost something irreplaceable in your life if your tooth is removed.
Losing any of your frontal teeth can also make you look older than your age, and trigger low self-esteem.
You may not feel confident to smile or talk in the public because of the missing teeth.
Exodontics can lead to bone loss around the extraction site and cause your mouth to shrink inward, making you look like a granny while talking.
Tooth extraction has Cosmetic effects
The more tooth you lose, the more the loss of gum and jaw bones, leads to poor facial support.
The jaw bones support the gum and teeth, and when some of them are lost, the facial skin becomes less intact and drops.
The lips droop, and hollow form in the cheeks due to the degeneration of the jaw bones, and you appear older than your age.
The Integrity of your Jawbones is at stake
Since you’re bound to lose some of your jaw bones over time due to the weakness of the root after tooth extraction, the teeth near the extraction site can fill the cavity.
When you have a problem with a such tooth in the future, it may be very difficult to extract.
Also, the reduction in the mass of your jaw bones can make it difficult for the dental surgeon to carry out any future tooth extraction when the jaw bones have degenerated and become thin and weak.
Risk of Osteoradionecrosis (ORN)
Patients with a history of illnesses that involve using radiation treatment around the head and neck have a risk of developing osteoradionecrosis after tooth extraction.
Osteoradionecrosis is one of the complications of radiation therapy causes death to the jaw bones underneath the extracted tooth due to the exposure of the blood vessels around the bone to radiation.